Molluscum: Everything You Need to Know About This Skin Infection
If you’ve ever woken up with odd, smooth and circular bumps plaguing different areas of your skin, it’s likely you may have fallen victim to molluscum, a common skin condition.
While this skin condition may not be too irritating, it is contagious and therefore, it’s important to understand exactly what molluscum is and how to treat it.
Here to answer some of the most common questions about molluscum is our very own Elizabeth Drumm, FNP-C, DCNP.
What is molluscum?
“Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a very common viral skin infection. MC may appear in any age group, including adulthood, although it is most commonly seen in children.”
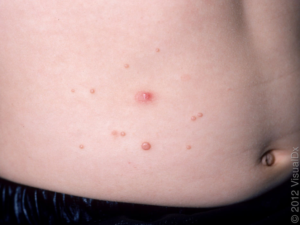
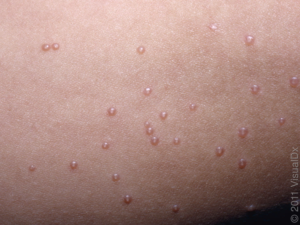
What does molluscum look like?
It presents as small, skin colored to pink, smooth bumps. Molluscum is typically not irritating or painful, although it may cause some itch. The lesions can grow larger over a few weeks. Due to a high risk for spreading the virus, the lesions may increase in number.
What causes molluscum?
“Molluscum is caused by a poxvirus that only affects humans.”
You can contract this virus in a number of different ways.
Using a towel that’s been infected with the virus can transfer is to you as well as skin-to-skin contact, using an infected razor, and coming into contact with the virus in any way.
Is molluscum contagious?
“Yes, molluscum is contagious and may pass to others by skin to skin contact or via touching contaminated clothing, towels, toys, and more. It may be spread to other areas on the body by scratching or picking at the lesions. It is also spread through sexual contact.”
Surrounding eczema or rash may accompany the molluscum. This may increase the risk of spreading due to the desire to scratch.
Avoid shaving if you have molluscum due to risk for transferring the virus along the route of the razor.
How is molluscum treated?
“Molluscum will resolve without treatment within months to years. Watchful waiting is a treatment option and may even be recommended depending on the location of the lesions and/or the age of the patient.”
However, due to the risk for spreading, there are treatment options for removal.
Here are a few common treatments for molluscum:
- Topical irritant agents: such as Retin-A (tretinoin) cream applied nightly. This may take a few weeks before seeing any improvement.
- Destructive treatments: such as liquid nitrogen “freeze spray” and cantharidin (canthacur) “beetle juice” solution. These will cause blistering and sores, which may be painful, with a goal to destroy the lesion. Canthacur is well tolerated in children, as it does not cause any pain during the clinic visit, although will cause sores at home.
- Removal of the lesions with scraping (curettage) during your clinic visit. This may be painful.
If you believe you have this common skin condition, book an appointment with your dermatologist to discuss treatment options!
About Elizabeth Drumm, FNP-C, DCNP
 Elizabeth received her Bachelor’s of Science in Nursing from the University of Illinois in Urbana-Champaign. While working as a pediatric nurse, she completed the Family Nurse Practitioner program and earned her Master’s Degree from DePaul University in 2013. Initially, Ms. Drumm practiced as a Nurse Practitioner in pediatric hematology/oncology.
Elizabeth received her Bachelor’s of Science in Nursing from the University of Illinois in Urbana-Champaign. While working as a pediatric nurse, she completed the Family Nurse Practitioner program and earned her Master’s Degree from DePaul University in 2013. Initially, Ms. Drumm practiced as a Nurse Practitioner in pediatric hematology/oncology.
Prior to joining Dermatology Associates of LaGrange, Ms. Drumm completed an intensive two-year Dermatology Nurse Practitioner Fellowship training at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center in Burlington, Massachusetts. During this time, she presented on topics in medical dermatology, spent time in dermatology specialty clinics, and attended weekly grand rounds and lectures at the Boston hospitals.
Elizabeth has extensive medical experience, ranging from child and adolescent health care to hematology and oncology, where she then found her passion for dermatology. She enjoys all aspects of medical dermatology, primarily skin cancer screening/prevention and skin rashes.
You can learn more about Elizabeth here.
References:

